What is a High ROI Business and How Can You Find One?

What is a High ROI Business and How Can You Find One?
In the world of business acquisitions, finding a high ROI (Return on Investment) business is the ultimate goal for many buyers, especially financial buyers. These buyers are driven by profitability and are on the lookout for businesses that can serve as vehicles to maximize their returns. But what defines a high ROI business, and how can you identify one?
Defining the High ROI Business
A high ROI business is one that delivers significant profits relative to the capital invested. These businesses typically have strong financial performance, efficient operations, and untapped growth potential. For buyers, a high ROI business represents an opportunity to enhance profitability further through strategic improvements.
From a buyer's perspective, a high ROI can be good for them as they can quickly repay the investment that was required to buy the business. As always, thorough due diligence is required as sometimes things may be "too good to be true".
On the other hand, a seller who has worked hard to create a good ROI relative to their industry will stand in a good position to sell their business quickly and to a genuine buyer. Understanding what a good ROI is and how to use that as part of your marketing strategy is important.
How is ROI Calculated in a Business Sale?
ROI is typically displayed in business for sale ads as a percentage, such as 40% ROI, this is calculated by dividing the annual net profit by the asking price, or highlighted in the financial summary, allowing buyers to assess the potential return on their investment.
Here is the calculation:

Examples of ROI in Business Sales:
- A business priced at $300,000 with an annual net profit of $200,000 has an ROI of 66.7%, meaning the payback period is 1.5 years.
- A business priced at $400,000 generating $200,000 in annual net profit has an ROI of 50%, resulting in a payback period of 2 years.
- A business priced at $500,000 generating $125,000 in annual net profit has an ROI of 25%, resulting in a payback period of 4 years.
- A business priced at $800,000 generating $400,000 in annual net profit has an ROI of 50%, meaning the payback period is 2 years.
- A business priced at $1,700,000 with an annual net profit of $578,000 has an ROI of 34%, allowing the investment to be recovered in 2.94 years.
You can explore more examples of businesses with high ROI by visiting Bsale's business listings.
So how can you take the ROI% and figure out how long it will take you to repay the investment?
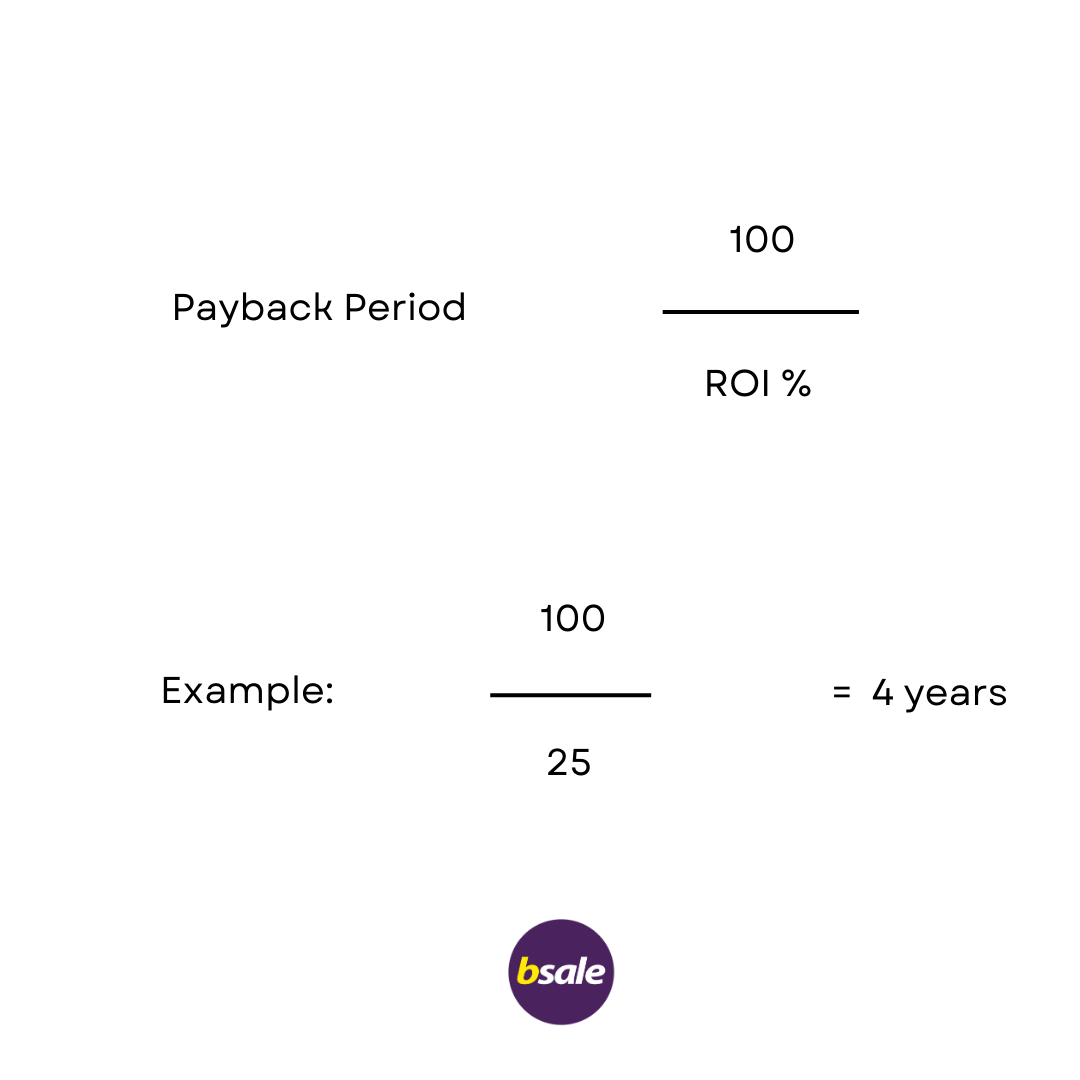
Here is a quick chart to show you how many years a it will take to repay a ROI %
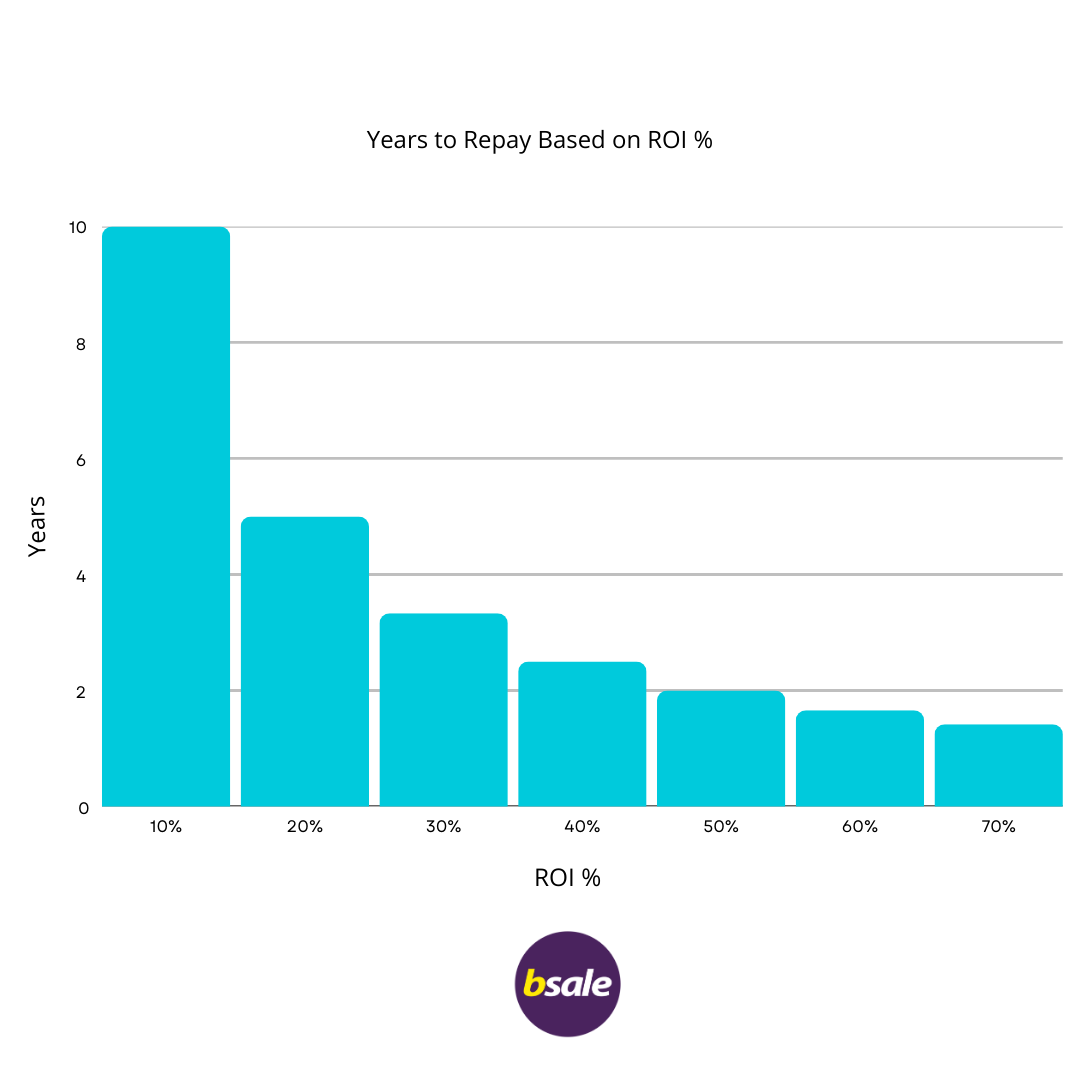
But of course, there are a number of variables. When you buy a business you assume it will continue at the same level of profitability (ideally increase). So you assume that the business will be repaying you (as the owner) this investment and it will be "paid back" after those years.
What is a Good ROI?
An ROI percentage that is too high, such as 70%, means the business could be paid off in as little as 8–9 months. While this might sound appealing, it’s essential to ask why the seller would want to part with such a profitable business. Often, it could indicate issues like a short lifespan after the sale, unstable foundations, or skewed financials due to the business being relatively new. These factors may suggest the business isn’t very stable or sustainable.
An ROI percentage that is too low, such as 15%, could mean the business is overpriced or that the seller is valuing it based on untapped potential or a "golden gem" rather than current profitability. Businesses with a low ROI, taking 6+ years to repay, might have hidden assets, patents, or growth opportunities that appeal to the right buyer. Examples include tech start-ups or competitor acquisitions, where the valuation is driven by future potential rather than past performance.
A well-placed ROI typically falls between 20–40%, representing a repayment period of 2.5–5 years. Most businesses for sale will sit within this range, with variations depending on the industry, type, and size of the business.
So, what is a good ROI? Many would argue it lies within the 20–40% range, but not all businesses are valued solely on financial history. ROI is calculated based on current financial data, so it’s vital to consider it alongside other factors, such as industry trends, market position, and growth potential, to fully understand the value and viability of the business.
Is ROI Used by Buyers to Compare Businesses?
ROI is a powerful tool for comparing businesses - but it is based solely on financial information.
ROI does offer a standardized measure of profitability as a percentage, regardless of size or industry which could allow comparisons. It highlights how efficiently a business generates profit relative to its asking price, making it easier to identify opportunities with higher returns and quicker payback periods. ROI also helps identify which businesses are performing better financially (as long as everything is accounted for accurately).
Buyers can use it to evaluate how well a business aligns with their financial goals, whether they prioritize quick returns or long-term growth. Additionally, comparing ROI against industry norms can identify outperforming opportunities or potential risks, enabling informed and strategic decision-making.
5 Factors That Can Impact your ROI, After you Buy.
So is a ROI guaranteed?
Well, no, of course not. It is a guide, based on previous financial history. A business is an evolving and changing system that requires good management and environment to continue its profitability.
The business’s financial performance after the purchase directly impacts ROI. Growth in revenue through better marketing or new customers can shorten the repayment period. Conversely, a decline in sales or market demand can delay it.
1. Operational Efficiency
Improving operational efficiency by cutting costs or streamlining processes can increase profits, accelerating ROI. However, unexpected expenses, such as rising costs or outdated equipment, can slow repayment.
2. Financing Terms
Loan terms play a big role. High-interest rates or repayment schedules with large upfront payments can reduce available cash flow, delaying ROI. Favorable financing terms, like lower rates, can speed up the repayment process.
3. Market Conditions
External factors like economic growth or downturns impact ROI. Booming markets can boost sales and profits, while recessions or inflation can reduce demand and delay repayment.
4. Buyer Involvement
Hands-on involvement by the buyer often leads to quicker improvements in sales and efficiency, speeding up ROI. Passive ownership, however, may miss growth opportunities, prolonging the repayment period.
5. Industry Trends
Shifts in industry trends, regulations, or technology can impact profitability. Businesses that adapt quickly are more likely to maintain strong ROI repayment schedules, while those that lag behind may face delays.
So Does an ROI Indicator Help Buyers?
ROI is a key metric for evaluating and comparing business opportunities, offering insights into profitability and payback potential.
Keyword... potential, which is based on previous financial history.
So does it help? Yes.
Is it the complete answer when buying a business? No.
Whether you’re a buyer seeking high returns or a seller looking to showcase your business’s value, understanding ROI is essential.
Explore high ROI opportunities on Bsale and discover businesses that align with your financial goals.As always, make sure you obtain professional advice when buying or selling a business in Australia.
Tags: buying a business buyer types of buyers
About the author

Vanessa Lovie
CEO Bsale Australia
Vanessa is the current manager and CEO of Bsale Australia. Over the past 11 years as a business owner, she understands what it takes to grow a ...









